From one Yandex disk to another. Backup to the cloud Yandex disk.Backup files to the cloud. Actions on files and folders in Yandex.Disk
Yandex stock quotes on the NASDAQ stock exchange fell by almost 10% shortly after the opening of trading. The fall in the price of securities is explained by the reaction of investors to the potential emergence of Sberbank as a shareholder of Yandex, analysts say.
Yandex shares on NASDAQ in New York by 20:35 Moscow time had fallen by more than 9.66% compared to the previous day, to $32.41, according to exchange data. The company's capitalization amounted to $10.6 billion, while on October 17 at the close of trading it reached $11.7 billion. By 00:22 Moscow time, Yandex's quotes on NASDAQ decreased by 17.8%, to $29.49 per share, or $9.6 billion for the entire company.
Earlier, The Bell reported that Sberbank is negotiating the purchase of a large stake in Yandex - up to 30% of the capital. According to the publication’s sources, in this way the state bank proposes to “protect the company from possible problems with competitors and with the state.” “Sberbank did not receive an offer to buy out Yandex shares and did not approach Yandex with such a proposal. This possibility is not being discussed,” the press service of Sberbank told Kommersant. “We do not comment on rumors,” the Yandex press service said.
The Internet company did not make such an offer to Sberbank, Kommersant’s interlocutor familiar with the situation is sure.
In Russia, Internet holdings continue to consolidate: an alliance was recently announced between Mail.ru Group and the Russian assets of the Chinese Alibaba Group, recalls Kommersant’s interlocutor at Sberbank. In his opinion, buying a stake in Yandex could be an “evolutionary and progressive step”, “so as not to miss the initiative.”
According to one federal official, the deal between Yandex and Sberbank could have been discussed at this week's Open Innovations forum in Skolkovo. “Probably, Yandex wants to move under the wing of Sberbank, which is an alternative government structure with its own special relationship to technology,” he believes. The recently intensified conflict between Yandex and media holdings over changes in anti-piracy legislation and the possible purchase by Sberbank of a stake in Yandex are unrelated processes, the federal official is sure.
The fall in Yandex's quotes is due to the emergence of information about the possible entry of Sberbank into its capital, according to analysts interviewed by Kommersant. The first question is what structure of the transaction is expected, whether new shares will be issued or there will be a buyout from existing shareholders, notes Uralsib analyst Konstantin Belov.
The actual control over Yandex is now with the founder Arkady Volozh and his partners, and the first question that arises among investors is whether a deal with Sberbank can change this, he believes.
“The market may be afraid that the management of the company will change and instead of the people who founded it, there will be one of the most progressive, but still a state bank,” says Konstantin Belov.
Yandex is a company in which the founder is the largest shareholder, investors usually like this, but on the contrary, they don’t like state participation, agrees Raiffeisenbank analyst Sergei Libin. A similar situation occurred with Magnit shares when it was announced that VTB Bank would buy out the stake of its founder Sergei Galitsky: as a result, Magnit’s quotes fell almost threefold, the analyst recalls.
Yandex has two classes of shares; Most likely, we can talk about the purchase of “super-voting” shares - Arkady Volozh and other employees have such papers, says Sergei Libin. “Buying 30% from the market is long, difficult and expensive. There is no point in carrying out an additional share issue, since it will dilute Yandex’s capital and reduce its value. This refers to a ransom from Arkady Volozh,” suggests Sergei Libin. According to his estimates, 30% of Yandex is worth about $3 billion.
There may be quite a large potential for cooperation between Yandex and Sberbank, since Yandex has a “good balance sheet” and there is no need for new financing, that is, partnerships between companies can be in joint projects, believes Konstantin Belov. An example of this is “Yandex.Money,” he reminds.
From an economic point of view, Sberbank’s purchase of Yandex shares is advisable, believes Sergei Libin. “Yandex shares will grow; Considering that they have fallen quite a lot recently, this is not a bad time to buy,” says Sergei Libin. But economic feasibility in this deal is not the main thing, he believes: for this, Sberbank can buy smaller companies with greater potential profitability as part of venture investments. “The motive is political,” the analyst believes.
Sberbank already has a “golden share” of Yandex - at the moment when the bank received it, the state already had a desire to somehow control Yandex,
and the golden share was “a compromise option in which control is minimal.” There is no direct participation of Sberbank in the capital of Yandex, but there is an instrument that gives the right to block some decisions that are objectionable to the state, he says. “It can be assumed that the state has always had a desire to control Yandex, and now conversations about this have begun again,” the analyst believes.
Vladislav Novy, Anna Afanasyeva
Beginner Internet users may be interested in what Yandex Disk is. Let me explain right away - this is cloud storage, disk space that is provided to any user with Internet access.
What is Yandex.Disk for?
It helps to store files that are rarely used on a personal computer (archives, program images, photographs).
Note! The amount of allocated disk space is usually 10 gigabytes.
Using Yandex Disk often saves valuable data that was previously backed up on your computer and in cloud storage.
For example, if the operating system does not start as a result of a failure or the hard drive is broken, the owner of the files can log into his Yandex account and download them to a new device. This precaution saves a lot of time and money.
All that remains is to learn how to use Yandex Disk - to get the opportunity to personally experience all the benefits of the project.
Registering a mailbox
Unfortunately, the creators of the service did not provide for the possibility of using Yandex Disk without mail. Therefore, you first need to register a personal mailbox:
Open the website www.yandex.ru and follow the “ ” link located in the corner of the page.
Enter your first and last name. You can use an invented pseudonym or real personal data, there is no difference.

To install Yandex.Disk, open an account on Yandex
- Create a username. It must consist of Latin letters and not duplicate an existing one.
- Set a strong password – When using a vault, it is important to pay attention to security.
- Click the “Register” button and wait until the server processes the request and creates an account.
Using Yandex Disk
It is not necessary to use a mailbox; it is only required to log into the cloud storage. It is located in the user tab under the “Disk” link; you can also go there by entering the address disk.yandex.ru in the browser line.

The screen will display a greeting to the new user and a notification that you have been provided with 10 gigabytes of disk space for eternal use. It can be freely used to save files in a wide variety of formats.
If the allocated 10GB is not enough for you, you have the opportunity to purchase additional gigabytes of disk space for money.

How to use Yandex Disk for the first time?
When we first log into Yandex.Disk, we are prompted to download an application for our computer (“Download Disk for Windows”). I think there is no need to rush to install the application. To begin with, it is better to evaluate all the advantages of the online version. Therefore, we say “thank you” and close the invitation window.

Next, go to the main “Files” tab. There you can upload or download data, as well as create new directories. To add your first file to cloud storage, just click on the appropriate button and select it on your computer.

The process of completing the task depends on the file size and the connection speed provided by the provider. When the operation is complete, a new item will appear in the main or preselected folder.

After this, the received address must be copied to the clipboard and forwarded to any user. Anyone can download the information via a direct link - even if he does not understand what Yandex cloud storage is and how to use it.
Program for Yandex Disk
You can use the storage service not only through the web interface, but also through the official program on your computer. But it’s better to do this when you master the online version of the disc.
The Yandex.Disk application is optimized for working with files. While a regular browser often makes mistakes when downloading large amounts of information and even closes automatically in the middle of the process.
You can download the application on the website https://disk.yandex.ru/client/disk and install it on your PC for free. Our instructions will help you with this:
Go to Yandex Disk and select your operating system from the list provided.

Download the installation image to your hard drive and run it by clicking on it.

Accept the license agreement, wait for installation, and the program will appear in the registry of your computer.
In the window that opens, you must enter your email address and password to gain access to your personal file storage.
After this, the main directory will be displayed with a list of files, as well as folders and partitions. To download new information, be it an archive, video or image, just drag it with the mouse into the program window and wait for the task to begin.

In general, working with storage elements is completely similar to the web interface, with the exception of increased data processing speed and high convenience.
A special feature of Yandex Disk installed on a computer is its integration into the operating system. After installation, the user will see that a new disk has appeared in the “My Computer” folder. It is on it that files uploaded to the cloud will be duplicated - for greater security.
If desired, Yandex Disk for Windows can be configured in detail, managing synchronization, the amount of allocated space and other important aspects. This makes the application flexible, functional and very user-friendly.
To configure Yandex.Disk, find the icon in the lower right corner of your computer screen. Click on it and go to the disk settings.

Next, by going to the settings, we can designate the folders that will be automatically synchronized. That is, their contents will be automatically duplicated in the Yandex disk cloud. To do this, go to the “synchronization” tab of the disk settings and uncheck the folders that do not need to be synchronized.

Thus, you have learned how to install and use Yandex Disk. This cloud storage will help you free up your computer's memory and protect your valuable files - but you will only need to pay money if you want to increase the size of the allocated space. And even a novice computer user can master the cloud. You just need to follow these instructions and have the desire to learn how to work with the service.
Over time, your computer or laptop accumulates enough a large number of files - 1000, 2000, or even 500,000. Their importance can be very high, especially if these are family photographs, videos, or work documents.
To reliably protect valuable files from viruses and damage As a result of a file system failure, each PC user needs to make a duplicate of their data at least once every 2-3 weeks - create backup copies. Having a “fresh” backup will help you restore information from it in case of loss.
Where to store backups: on an external HDD or trust the cloud?
When there were no “clouds” yet, backup copies were usually stored:
- on local PC
- external (removable) USB drive, flash drive or DVD
- on a server on the local network
- on a remote FTP server
Advanced users and system administrators also copied files to remote servers using FTP / SSH / WebDAV, etc. protocols. Now there is an additional opportunity - to store folders on the Internet, on a server from the Yandex company.
What is Yandex Disk?
I am index drive is a cloud service that allows you to store files on a server under your account. By default, you are provided with 10 GB of disk space free of charge and forever, with the possibility of further increase. Due to its accessibility and convenience, this service quickly gained popularity and, as of October 2018, it is already used by more than 16 million users.
Benefits of Cloud Storage
- Storing files outside the office (outside the home) helps protect data from fire and viruses
- High reliability, since folders are additionally backed up by Yandex, and transmission is carried out using a secure protocol
- Availability of data from anywhere in the world
- High trust, since the Yandex company has been working in the IT market for many years - it is a leader in the field of IT and Internet services in Russia and the CIS countries.
Flaws
- The resource is limited to 10 GB, increasing the size is paid
- Very secret (confidential) information that represents a trade secret is still not recommended to be stored in the clouds
Whether to store backups online or not is up to you. If you are an ordinary user who has not very sensitive data and its volume is about 3 - 6 GB (does not exceed 10 GB), then backup to Yandex.Disk is an excellent free solution for ensuring the safety of document files, photo and video backup! As a rule, the specified volume is sufficient to store several copies of the most important files.
Exiland Backup - a simple cloud backup tool
This concludes my brief overview of the opportunity. If you have any questions, I will be happy to help. Write to me via the feedback form.
Mikhail, Exiland Backup developer
Today we present the long-awaited Yandex.Disk client for Linux. One could even say “especially for Habrahabr,” since not a single mention of Disk here was complete without questions about the client for Linux.
It has all the basic functionality that clients for OS X and Windows have, and even more (symlinks!), and one feature - it is console-based.
Read below about how it is configured, what exactly it can do, and how exactly it is designed and what was difficult to do in it.
You can install it. Immediately after installing the package, the command will appear in the terminal yandex-disk, through which communication with the Yandex cloud subsequently takes place. After this you need to manually run the command setup.
The settings wizard allows you to select a folder for synchronization in dialog mode, enable autorun at system startup, configure work through a proxy server (if, of course, you use one) and log in to Yandex.Disk. When setting up manually, the first thing you need to do is log in. After this, a config will be created in the .config folder located in the home directory, in which you can configure the path to the synchronization folder (you can specify it manually in the console), specify the path to the token file, specify the folders that will or will not be synchronized, and specify proxy server settings.
Selective synchronization is possible in Yandex.Disk. Team exclude will allow you to exclude the folder from synchronization: all changes made in it after this will not be sent to the cloud.
Option read-only will allow you to change files locally, without uploading them to the cloud. If conflicts arise with local changes, the latter will be saved in renamed files, and changes from the cloud will be synchronized. Option overwrite will overwrite locally modified files in read-only mode.
We can't help but boast about the most interesting innovation in the synchronization core - from now on we support synchronization of symlinks! If you encounter any difficulties or questions in using the command console client man And help will help you understand them in a simple and accessible way.
How it's made
So that in the future the code could be used to implement clients for different operating systems, it was decided to write it in C++. We moved pieces of code specific to different operating systems into separate functions or classes, and wrote their own implementation for each platform. We took Boost, OpenSSL and as the main cross-platform libraries, and git became the version control system. The Linux client was built using autoconf. The code was written and debugged in a combination of KDevelop + console gdb, or in Qt Creator (depending on the preferences of the developer).Interaction with the cloud and synchronization are carried out using the Yandex.Disk core library, which is used by desktop clients of the service.
How does it work
The console client consists of two parts: the daemon and the client. They communicate via text packets containing json messages sent via sockets (unix-domain sockets are used on Linux and Mac OS X). Asynchronous work is implemented using the boost::asio library. Data access synchronization is implemented through boost::asio::io\_service::strand, which eliminates the problem of simultaneous data access by multiple threads and also eliminates the appearance of deadlocks.For localization we use the boost::locale library. The text inside the client is encoded in utf-8 and, if necessary, is converted in code specific to each operating system. Filesystem monitoring for Linux uses inotify, which fits nicely into the asynchronous operation of boost::asio.
How does synchronization work?
Synchronization is the heart of Yandex.Disk, its key feature. The task of synchronizing a file tree with the cloud is divided into several independent parts.1 . File system monitoring. The Yandex.Disk synchronization kernel was designed and created as a portable abstraction capable of performing assigned tasks on all supported platforms. But such a problem as file system monitoring is not implemented either by the standard C++ library or even by such monsters as boost. Moreover, even using the “native” API of the operating system, we receive a set of events specific to each platform.
To monitor the file system, an “observer” interface was designed that can monitor events in a specific directory and return a list of events that occurred in it. Moreover, the set of these events is different for each supported platform. For example, Mac OS X can only report the fact of some change in one of the child directories without detailing it. But Windows and Linux return the full set, including creating, deleting, modifying and moving objects. Although practice has shown that events on the Windows platform should not be trusted and the most reliable option remains listing the directory after receiving an alert.
2 . Indexing local files and directories. To control the integrity and implement delta file updates, the Yandex.Disk synchronization kernel uses digests - sets of checksums of a file and its individual parts. For the entire file, we calculate a strong SHA-256 hash and a set of less persistent sums for individual blocks. Each file located in the Yandex.Disk folder and not included in the exclusion list must be indexed. But calculating the SHA-256 hash is a fairly expensive operation, and calculating hashes every time the software is launched would be an unforgivable waste of resources. Therefore, after file indexing is completed, the synchronization kernel saves the received digest in a “bank” - a special storage located in the Yandex.Disk service directory. To search for digests in the storage, a unique file identifier is used - inode (size and last modified time). Unfortunately, this approach is not without its drawbacks. For example, many crypto container files keep the last modification time unchanged even after being written.
Probably, except for the intricacies of working with symbolic links, nothing in the listing of directories is of particular interest. For synchronization to complete successfully, the kernel must detect and exclude cyclic branches from synchronization.
In general, symbolic links are a real headache for the synchronization kernel. They can point to arbitrary locations in the file system, and the same synchronization rules cannot be applied to all of them. For example, Mac OS X application packages very often contain symbolic links to system library directories, and synchronizing them to the cloud would be undesirable - especially between different versions of the OS. But at the same time, the ability to synchronize additional directories using symbolic links is a very tempting opportunity that I didn’t want to miss.
Therefore, a special policy was introduced for the synchronization of symbolic links, thanks to which the kernel can choose a specific synchronization option for each symbolic link - depending on the location of the object to which it points.
3 . Getting the cloud file system tree. To solve the synchronization problem, it is not enough to have a local file structure and file digests - you need to get the current state of the file system in the cloud. If the synchronization engine had to traverse the tree using the PROPFIND method each time, each synchronization cycle would take an unreasonably long time and create unnecessary load on the channel. Therefore, Yandex.Disk software uses a special API, which makes it possible to obtain the current state of the file tree in the cloud and the changes that have occurred in it, starting from a certain known moment, determined by the version of the tree.
4 . Receive alerts when your cloud file system changes. Real-time file synchronization requires timely notification of changes to files in the cloud. It would be possible to use periodic polling of the server by clients, but after assessing the possible number of clients, we came to the conclusion that this approach would be poorly scalable and would quickly overload the service infrastructure. After some searching, we settled on the XMPP protocol. One of its implementations has been working in Yandex for a long time. It was developed by a team that later created a WebDAV server for the Yandex.Disk project, so there were no difficulties with the integration of this protocol.
Currently, push notifications processed by the synchronization core include not only events that occurred directly with files or folders in the Yandex.Disk cloud, but also various service messages. For example, about the issuance of additional space or the actions of other users in shared folders. Adding these events to the existing protocol did not cause much difficulty due to the extensibility of XMPP, which once again confirmed the correctness of our choice.
5 . Creating a list of synchronization operations. Once the synchronization kernel has both file trees at its disposal - local and remote - you can begin the synchronization procedure itself. To do this, a special algorithm for comparing trees is used, which takes as input, in addition to the two mentioned trees, also a third one - the last synchronized one. The result of the algorithm is a list of operations that need to be performed on local and remote files and directories to bring the trees to a common form.
6 . Processing the sync queue. The list of operations for local and remote trees is created independently. This may result in conflicting operations. For example, deleting a file in the cloud that has been changed in it and has not yet been synchronized locally, or changing a file simultaneously locally and in the cloud. Mod/delete conflicts are always resolved by the kernel in favor of the modification, and double modification conflicts are resolved by renaming one version of the file. In this way, we can guarantee the safety of the data and give the user the opportunity, after synchronization is complete, to decide which of the changes suits him best in each specific case.
Synchronization operations must follow a strict order; a file cannot be transferred until its parent directory has been created. Also, a directory cannot be deleted while there are files inside it that need to be moved to a new location. The tree comparison algorithm already creates operations in the required order, but if errors occur, it can break down. To prevent this situation, each operation has a list of dependencies - a set of operations that must complete before it can begin, and a set of operations that must not begin until it completes.
In addition to dependencies, the order in which operations are performed is influenced by their priority. For example, file transfer operations are performed based on file sizes - from small to large.
All these tasks are performed simultaneously, imposing additional requirements on the quality of synchronization of parallel processes and the distribution of resources within the Yandex.Disk synchronization kernel. If you don’t have Ya.Disk yet, you can get one
Good day everyone! Today we are talking about a very convenient service that I have been using in my work for a long time - Yandex Disk. What kind of “beast” is this? - you might ask. I will talk about this in detail in the article below. If you have any questions, ask them in the comments, we will figure it out and look for answers! In the meantime, let's get acquainted with one of the most convenient file storages from the developers of the popular Russian search engine Yandex.
1. Yandex Disk: what is it
Yandex.Disk is a popular cloud storage that allows users to store various information (photos, videos, audio, texts and other files) in the so-called “cloud”, i.e. on a server on the network. Data stored on Yandex.Disk can be shared with other users, as well as accessed from various devices - other computers, tablets and smartphones. The basic version of Yandex.Disk is completely free and available to everyone. I remember that in 2012, registration was by invitation only, and I used an alternative service - Dropbox. But now I have completely switched to Yandex Disk Cloud. After all, free, and even accessible from everywhere, 10 GB is never superfluous.
2. Yandex Disk: how to use - step-by-step instructions
So, I convinced you, and you decided to install Yandex Disk on your computer. Now let’s take a closer look at how to use Yandex Cloud (also called Yandex.Disk, since it is a cloud data storage).
2.1. How to create Yandex Disk (registration in Yandex Cloud)
In order to start using Yandex.Disk, you need register and create a mailbox from Yandex(if you already have one, go straight to the second point).
4. Installing Yandex.Disk on a smartphone. Free apps are available for iOS and Android, so you can easily download them from the App Store and Google Play. The application for iOS does not have a very high rating, there are some shortcomings, all of which can be seen in the reviews.

2.3. Yandex Disk: how much free space?
Immediately after registering and installing Yandex.Disk, you can access 10 free GB of space in the Cloud. This is quite enough for a start; it lasted me about six months. What to do if there is not enough space?
- Additional free 10 GB for inviting friends. You can get 512 MB of free cloud space for each friend you invite. Go here - https://disk.yandex.ru/invites and you will see your referral link, which you need to copy and send to your friends. After each user registers using your link, you will receive additional disk space, and the invited friend will receive an additional 1 GB.

- Additional up to 250 GB as a gift from Yandex partners. Various promotions are regularly held that will allow you to get additional gigabytes of free space. You can track current promotions on this page.
And of course, as you can expect from Yandex, additional space can be purchased. However, the pleasure does not come cheap:

If you need a lot of space in the Cloud, but don’t want to pay, you can create several mailboxes and create Yandex.Disk for each of them.
2.3. Login to Yandex Disk
Registration has been completed, the available space has been sorted out, the question arises - ?
You can view downloaded files in several ways:
1. Open the Yandex.Disk folder shortcut on the Desktop, if you did not delete it after installation.
2. Open Yandex.Disk in the My Computer folder.
3. Click on the Yandex.Disk icon in the taskbar, located in the far right corner of the screen.

4. Log in to your Yandex mail through any browser and at the top there will be a link to the Cloud:
6. Go to the Yandex main page while logged in to your email. In the upper right corner there will be a link to Yandex.Disk:

2.4. How to upload files to Yandex Disk - 7 easy ways
Let us now consider the most important point, because of which we took all these actions -. Again, there are several ways to do this:
1. Via context menu. Select the file that needs to be uploaded to the Cloud, right-click on it and select the item: “Yandex.Disk: Copy public link”:

2. Copy the file to the Yandex.Disk folder(I wrote above how to enter it). By default, this folder is synchronized automatically, so when you copy there, all files will be immediately added to your Disk.
3. Upload files via mobile app iOS or Android. I can consider this method in a separate article, if you leave such a wish in the comments.
4. Upload a file to the Cloud via browser. To do this, simply drag and drop the selected files into a browser window with Yandex.Disk open:

5. Copying other people's files. If someone shared with you a link to a file that is stored on Yandex.Disk, you can easily save it to your Cloud. To do this, you need to follow the sent link like https://yadi.sk/*** and click on the “Save to Yandex.Disk” button on the right.


They also often ask - how to upload a folder to Yandex Disk. The principle is the same as stated above in the files section. But there is one more additional advantage - the folder can be assigned to Shared access. This way, other users to whom you grant access rights will be able to view and download files in this folder, as well as upload their own files there.
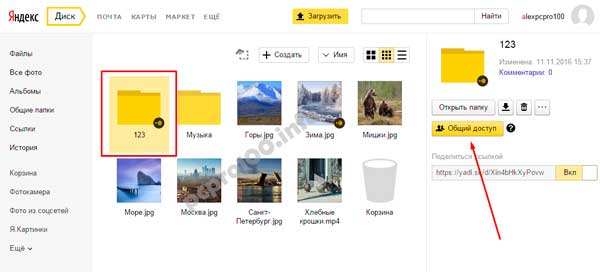
How to upload a video to Yandex Disk?– is also a very popular question from Cloud users. This is due to the fact that video files are usually large, and many people worry that they simply won’t “fit” and cannot be stored there. This is not true, video files, just like photos, can be uploaded and stored on Yandex.Disk.
2.5. Yandex Disk: how to transfer files to another user

You can also remove access to the file by clicking the mouse and switching it to the OFF position.
If for some reason you need to remove Yandex.Disk from your computer, then you should do the same as with a regular application - use standard operating system tools.
Let's move on: Start -> Control Panel -> Programs and Features
In the window that appears, select Yandex.Disk (usually it is the last one in the list) and click the “Delete” button. The downloaded files will remain in your account; only the application will be deleted from your computer.




